Hilt dependencies
To use Hilt, add the following build dependencies to the Android Gradle module’s
build.gradle file:
dependencies {
implementation 'com.google.dagger:hilt-android:2.59.2'
annotationProcessor 'com.google.dagger:hilt-compiler:2.59.2'
// For instrumentation tests
androidTestImplementation 'com.google.dagger:hilt-android-testing:2.59.2'
androidTestAnnotationProcessor 'com.google.dagger:hilt-compiler:2.59.2'
// For local unit tests
testImplementation 'com.google.dagger:hilt-android-testing:2.59.2'
testAnnotationProcessor 'com.google.dagger:hilt-compiler:2.59.2'
}
Using Hilt with Kotlin
If using Kotlin, you have the choice of using either KSP or kapt.
If using KSP, then apply the
KSP plugin in your root
build.gradle file.
Otherwise if using kapt, then apply the
kapt plugin in your root
build.gradle file.
plugins {
// Choose an appropriate version to replace the X.X.X
id 'com.google.devtools.ksp' version 'X.X.X' apply false
}
plugins {
// Choose an appropriate version to replace the X.X.X
id 'org.jetbrains.kotlin.kapt' version 'X.X.X' apply false
}
Then declare the Hilt compiler dependency using ksp or kapt respectively
instead of annotationProcessor.
Additionally if using kapt, configure it to correct error types by setting
correctErrorTypes
to true.
plugins {
id 'com.google.devtools.ksp'
}
dependencies {
implementation 'com.google.dagger:hilt-android:2.59.2'
ksp 'com.google.dagger:hilt-compiler:2.59.2'
// For instrumentation tests
androidTestImplementation 'com.google.dagger:hilt-android-testing:2.59.2'
kspAndroidTest 'com.google.dagger:hilt-compiler:2.59.2'
// For local unit tests
testImplementation 'com.google.dagger:hilt-android-testing:2.59.2'
kspTest 'com.google.dagger:hilt-compiler:2.59.2'
}
plugins {
id 'org.jetbrains.kotlin.kapt'
}
dependencies {
implementation 'com.google.dagger:hilt-android:2.59.2'
kapt 'com.google.dagger:hilt-compiler:2.59.2'
// For instrumentation tests
androidTestImplementation 'com.google.dagger:hilt-android-testing:2.59.2'
kaptAndroidTest 'com.google.dagger:hilt-compiler:2.59.2'
// For local unit tests
testImplementation 'com.google.dagger:hilt-android-testing:2.59.2'
kaptTest 'com.google.dagger:hilt-compiler:2.59.2'
}
kapt {
correctErrorTypes true
}
Hilt Gradle plugin
The Hilt Gradle plugin runs a bytecode transformation to make the APIs easier to
use. The plugin was created for a better developer experience in the IDE since
the generated class can disrupt code completion for methods on the base class.
The examples throughout the docs will assume usage of the plugin. To configure
the Hilt Gradle plugin first declare the dependency in your project’s root
build.gradle file:
buildscript {
repositories {
// other repositories...
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
// other plugins...
classpath 'com.google.dagger:hilt-android-gradle-plugin:2.59.2'
}
}
then in the build.gradle of your Android Gradle modules apply the plugin:
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
apply plugin: 'com.google.dagger.hilt.android'
android {
// ...
}
Apply Hilt Gradle Plugin with Plugins DSL
To configure the Hilt Gradle plugin with Gradle’s new
plugins DSL
, add the plugin id in your project’s root build.gradle file:
plugins {
// other plugins...
id 'com.google.dagger.hilt.android' version '2.59.2' apply false
}
then apply the plugin in the build.gradle of your Android Gradle modules:
plugins {
// other plugins...
id 'com.android.application'
id 'com.google.dagger.hilt.android'
}
android {
// ...
}
Warning: The Hilt Gradle plugin sets annotation processor arguments. If you are using other libraries that require annotation processor arguments, make sure you are adding arguments instead of overriding them. See below for an example.
Why use the plugin?
One benefit of the Gradle plugin is that it makes using @AndroidEntryPoint and
@HiltAndroidApp easier because it avoids the need to reference Hilt’s
generated classes.
Without the Gradle plugin, the base class must be specified in the annotation and the annotated class must extend the generated class:
@HiltAndroidApp(MultiDexApplication.class)
public final class MyApplication extends Hilt_MyApplication {}
@HiltAndroidApp(MultiDexApplication::class)
class MyApplication : Hilt_MyApplication()
With the Gradle plugin the annotated class can extend the base class directly:
@HiltAndroidApp
public final class MyApplication extends MultiDexApplication {}
@HiltAndroidApp
class MyApplication : MultiDexApplication()
Aggregating Task
The Hilt Gradle plugin offers an option for performing Hilt’s classpath
aggregation in a dedicated Gradle task. This allows the Hilt annotation
processors to be
isolating
so they are only invoked when necessary. This reduces incremental compilation
times by reducing how often an incremental change causes a rebuild of the Dagger
components. Enabling this option also enables
sharing test components and
classpath aggregation. Note that this option replaces
enableExperimentalClasspathAggregation since it has the same benefits without
any of its caveats.
To enable the aggregating task, apply the following configuration in your
Android module’s build.gradle:
hilt {
enableAggregatingTask = true
}
Applying other processor arguments
The Hilt Gradle plugin sets annotation processor arguments. If you are using other libraries that require annotation processor arguments, make sure you are adding arguments instead of overriding them.
For example, the following notably uses += to avoid overriding the Hilt
arguments.
javaCompileOptions {
annotationProcessorOptions {
arguments += ["foo" : "bar"]
}
}
If the + is missing and arguments are overridden, it is likely Hilt will
fail to compile with errors like the following: Expected @HiltAndroidApp to
have a value. Did you forget to apply the Gradle Plugin?
Local test configuration (AGP < 4.2 only)
Warning: This flag should only be used with AGP < 4.2. Newer versions of AGP no longer need this flag.
When the Android Gradle plugin (AGP) version used in the project is less than
4.2, then the Hilt Gradle plugin by default, will only transform instrumented
test classes (usually located in the androidTest source folder), but an
additional configuration is required for the plugin to transform local jvm
tests (usually located in the test source folder).
To enable transforming @AndroidEntryPoint classes in local jvm tests, apply
the following configuration in your module’s build.gradle:
hilt {
enableTransformForLocalTests = true
}
Note that the enableTransformForLocalTests configuration only works when
running from the command line, e.g. ./gradlew test. It does not work when
running tests with Android Studio (via the play button in the test method or
class). There are a few options to work around the issue.
The first option is to upgrade the AGP version in your project to 4.2+.
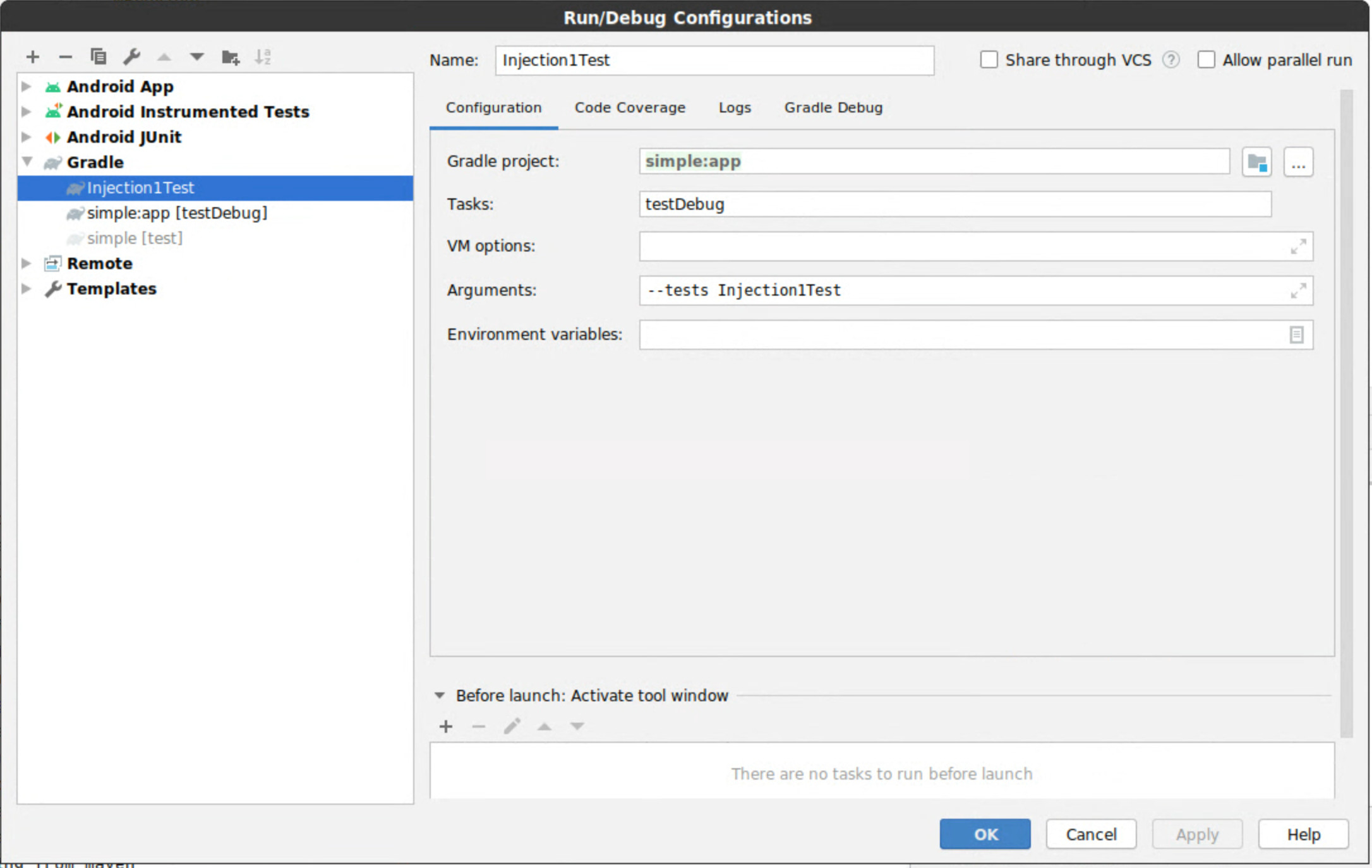
The second option, is to create your own Android Studio configuration that executes tests via the Gradle task. To do this, create a new ‘Run Configuration’ of type ‘Gradle’ from within Android Studio with the following parameters:
Gradle project: the Gradle module where the tests are locatedTask: the test task (usually eithertestortestDebug)Arguments: the list of tests (e.g.--tests MyTestClassSee)
As an example, see the setup below:
Classpath Aggregation (Deprecated)
Warning: This flag is deprecated and will be removed in a future release of Dagger. Use enableAggregatingTask instead.
The Hilt Gradle plugin also offers an experimental option for configuring the
compile classpath for annotation processing such that Hilt and Dagger are able
to traverse and inspect classes across all transitive dependencies from within
the application Gradle module. We recommend enabling this option because without
it, an implementation dependency may drop important information about
@InstallIn modules or @EntryPoint interfaces from the compile classpath.
This can lead to subtle and/or confusing errors, that in the case of
multibindings may only manifest at runtime. With this option enabled,
implementation dependencies don’t have to be relaxed to api. Note that this
option might have a build performance impact due to an increase in compilation
classpath. For more context on the problems this solves, see issues
#1991 and
#970.
Warning: If the Android Gradle plugin version used in the project is less
than 7.0 then android.lintOptions.checkReleaseBuilds has to be set to false
when enableExperimentalClasspathAggregation is set to true due to an
existing bug in prior versions of AGP.
To enable classpath aggregation, apply the following configuration in your
Android module’s build.gradle:
hilt {
enableExperimentalClasspathAggregation = true
}